Contents
Application architecture
Kaspersky Security is supplied as two images of SVM (secure virtual machine):
- Image of the SVM with the File Threat Protection component
- Image of the SVM with the Network Threat Protection component
An SVM (secure virtual machine) is a virtual machine on which a component of Kaspersky Security is installed. An SVM is deployed on a VMware ESXi hypervisor. For protection and scanning, the application does not need to be installed on each virtual machine.
Kaspersky Security components are registered as services in VMware NSX Manager:
- The File Threat Protection component is registered as a file system protection service (Kaspersky File Antimalware Protection).
- The Network Threat Protection component is registered as a network protection service (Kaspersky Network Protection).
Kaspersky Security services are deployed on the VMware cluster during installation of the application. When Kaspersky Security services are deployed, SVMs with Kaspersky Security components are deployed on each hypervisor in the cluster (see the figure below).
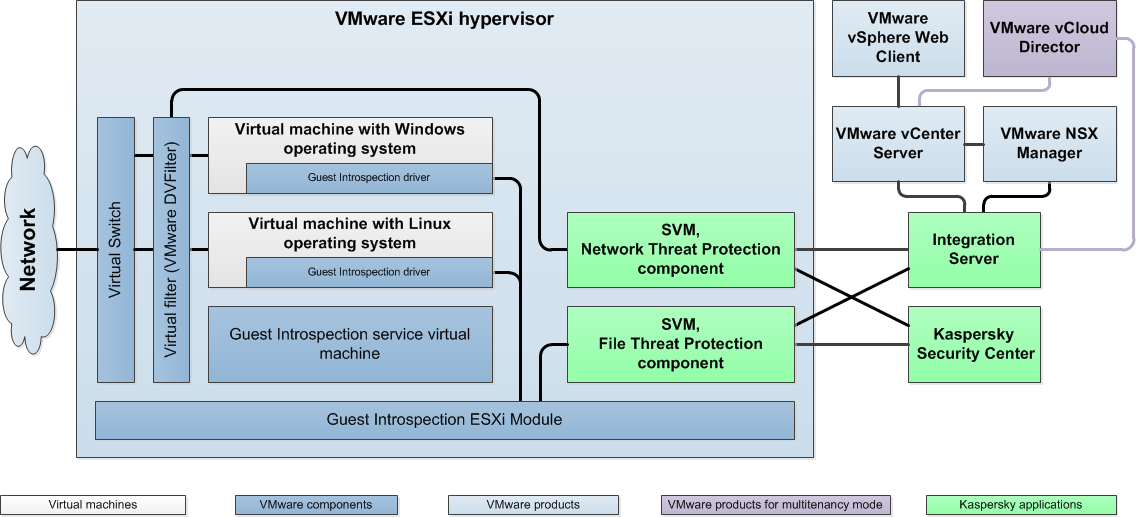
Application architecture
SVMs with the File Threat Protection component provide the following:
- Protection against viruses and other malware for all virtual machines that meet the conditions for protection of virtual machines.
- Anti-virus scanning of files of all virtual machines that meet the conditions for scanning virtual machines.
SVMs with the Network Threat Protection component provide protection against network threats for all virtual machines that meet the conditions for protection of virtual machines against network threats.
The Integration Server component enables interaction between the VMware virtual infrastructure and Kaspersky Security components.
The application is managed through Kaspersky Security Center, which is the remote centralized system for managing Kaspersky applications. Kaspersky Security interacts with Kaspersky Security Center via Network Agent, which is a component of Kaspersky Security Center. Network Agent is included in the SVM image.
The Kaspersky Security main administration plug-in provides the interface for managing the Kaspersky Security application through Kaspersky Security Center. If the application is operating in
, the Kaspersky Security administration plug-in for tenants is also required for application management.Kaspersky Security administration plug-ins are included in the Kaspersky Security distribution kit.
Kaspersky Security administration plug-ins must be installed on the computer hosting the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Console.
Contents of the Kaspersky Security SVM images
The image of an SVM with the File Threat Protection component includes the following:
- CentOS 7.6 operating system.
- File Threat Protection component of Kaspersky Security.
- EPSEC library. A component provided by VMware. The EPSEC library provides access to the files on virtual machines protected by Kaspersky Security.
- Network Agent. A component of Kaspersky Security Center. Network Agent interacts with the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server enabling Kaspersky Security Center to manage Kaspersky Security.
The image of an SVM with the Network Threat Protection component includes the following:
- CentOS 7.6 operating system.
- Network Threat Protection component of Kaspersky Security.
- Guest Introspection SDK. A component provided by VMware. Guest Introspection SDK enables monitoring network traffic of virtual machines at the network packet level and creating virtual filters.
- Network Agent. A component of Kaspersky Security Center. Network Agent interacts with the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server enabling Kaspersky Security Center to manage Kaspersky Security.
Application usage options
Protecting a virtual infrastructure managed by one or more VMware vCenter Servers
SVMs with Kaspersky Security components are deployed on VMware ESXi hypervisors managed by one or more standalone VMware vCenter Servers and protect the virtual machines running on these hypervisors. The application operates in normal mode.
The Kaspersky Security main administration plug-in is required for application management. You can use the main administration plug-in to configure individual settings for protecting a virtual infrastructure managed by each VMware vCenter Server or general settings for protecting the entire virtual infrastructure.
Protecting a virtual infrastructure managed by VMware vCloud Director
SVMs with Kaspersky Security components are deployed on VMware ESXi hypervisors managed by VMware vCenter Servers connected to the VMware vCloud Director Server. SVMs can protect all virtual machines operating within the virtual infrastructure, including virtual machines that are part of a vCloud Director organization.
This application usage option lets you protect isolated virtual infrastructures of tenant organizations or divisions of one organization (hereinafter also referred to as "tenants"). The application operates in multitenancy mode, which means that one instance of the application installed in the infrastructure of the anti-virus protection provider (hereinafter also referred to as the "provider") simultaneously provides multiple tenants with the capability for independent management of the protection of their virtual infrastructure.
The Kaspersky Security main administration plug-in and administration plug-in for tenants are required for application management. The main administration plug-in lets you configure the general application settings, Network Threat Protection settings, and the File Threat Protection settings of those virtual machines that are not part of vCloud Director organizations, such as the virtual machines of the provider. The administration plug-in for tenants lets you configure the individual settings of File Threat Protection for each tenant.
Virtual Administration Servers of Kaspersky Security Center are used to manage protection of tenants. The provider's administrator creates a separate virtual Administration Server for each tenant and provides the tenant's administrator with access to it. The tenant's administrator can use the virtual Administration Server and administration plug-in for tenants to manage File Threat Protection of their virtual infrastructure. The provider handles management of network protection, application database updates, application activation, and management of file copies placed in Backup.
The provider's administrator can obtain information about the protection of tenants' virtual machines by utilizing the report available on the Integration Server. However, report generation is disabled by default. To find out how to enable data logging to a report and export the report to a file in CSV format, please refer to the Knowledge Base.
The application installation procedure depends on the selected application usage option. It is recommended to select the application usage option before starting the installation. If you decide to switch to using the application in multitenancy mode after installing the application in an infrastructure managed by one or more VMware vCenter Servers, to ensure correct operation of the application you need to perform the additional steps described in the Knowledge Base.
Page topIntegration of Kaspersky Security components with VMware virtual infrastructure
Requirements for integration of Kaspersky Security components with VMware virtual infrastructure:
- Virtual infrastructure administration server (VMware vCenter Server, VMware vCloud Director). The component performs administration and centralized management of a VMware virtual infrastructure. The component participates in the deployment of Kaspersky Security. The virtual infrastructure administration server sends the Integration Server information about the VMware virtual infrastructure that is required for operation of the application.
- VMware NSX Manager. The component enables registration and deployment of Kaspersky Security services.
- Virtual filter (VMware DVFilter). This component lets you intercept incoming and outgoing network packets in the traffic of protected virtual machines.
- Guest Introspection driver (NSX File Introspection Driver). The component collects data on virtual machines and transmits files to Kaspersky Security for scanning. To enable Kaspersky Security to protect virtual machines, the NSX File Introspection Driver must be installed on these virtual machines. For more details please refer to documentation attached to VMware products.
- Guest Introspection service and Guest Introspection ESXi Module. The components enable interaction between SVMs and the Guest Introspection driver installed on the virtual machine.
The File Threat Protection component interacts with the VMware virtual infrastructure in the following way:
- The user or any application opens, saves, or runs files on a virtual machine that is protected by Kaspersky Security.
- The Guest Introspection driver intercepts information about these events and relays it to the Guest Introspection service.
- The Guest Introspection service relays information about received events to the File Threat Protection component installed on the SVM.
- The File Threat Protection component scans files that the user or an application opens, saves, or runs on a protected virtual machine:
- If no viruses or other malware are detected in the files, Kaspersky Security grants access to the files.
- If the files contain viruses or other malware, Kaspersky Security performs the action that is specified in the settings of the protection profile assigned to this virtual machine. For example, Kaspersky Security disinfects or blocks a file.
Interaction between the Network Threat Protection component and the VMware virtual infrastructure depends on the traffic processing mode that you selected during registration of the network protection service (Kaspersky Network Protection). If you selected the standard traffic processing mode, the Network Threat Protection component interacts with the VMware virtual infrastructure as follows:
- The virtual filter (VMware DVFilter) intercepts inbound and outbound network packets in the traffic of protected virtual machines and redirects them to the Network Threat Protection component installed on SVMs.
- The Network Threat Protection component scans network packets to detect activity typical of network attacks and suspicious network activity that may be a sign of an intrusion into the protected infrastructure, and scans all web addresses in requests over the HTTP protocol to check if they belong to the web address categories that should be detected according to the Web Addresses Scan settings.
If Kaspersky Security does not detect a network attack, or suspicious network activity, or a web address belonging to the web address categories selected for detection, it allows transfer of the network packet.
If a network threat is detected, Kaspersky Security does the following:
- If activity typical of network attacks is detected, Kaspersky Security will perform the action that is specified in the settings of the policy. For example, Kaspersky Security blocks or allows network packets coming from the IP address from which the network attack originated.
- If suspicious network activity is detected, Kaspersky Security performs the action that is specified in the policy settings. For example, Kaspersky Security blocks or allows network packets coming from the IP address from which the network attack originated.
- If a web address belongs to one or more of the web address categories selected for detection, Kaspersky Security performs the action that is specified in the policy settings. For example, Kaspersky Security blocks or allows access to the web address.
If you selected monitoring mode during registration of the network protection service (Kaspersky Network Protection), the Network Threat Protection component receives a copy of the traffic of virtual machines. When signs of intrusions or attempts to access dangerous or undesirable web addresses are detected, Kaspersky Security does not take any actions to prevent the threats but only relays information about the events to the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server.
Page topAbout the Integration Server
The Integration Server is a Kaspersky Security component that enables interaction between Kaspersky Security components and a VMware virtual infrastructure.
The Integration Server is used for performing the following tasks:
- Registration of Kaspersky Security services in VMware NSX Manager: the file system protection service (Kaspersky File Antimalware Protection) and the network protection service (Kaspersky Network Protection). Kaspersky Security services are required for installation of application components in a VMware infrastructure.
The settings required for registration and deployment of Kaspersky Security services are entered in a Wizard that is started from the Integration Server Console.
- Configuring new SVMs and reconfiguring previously deployed SVMs. The Integration Server sends SVMs the settings that you specify in the Integration Server Console.
- Retrieval of information about a virtual infrastructure (about hypervisors and virtual machines operating on each hypervisor) from VMware vCenter Server and transmission of retrieved information to application components. The Kaspersky Security administration plug-in and SVMs query the Integration Server for information about the virtual infrastructure.
- Configuring the list of mappings of vCloud Director organizations to virtual Administration Servers of Kaspersky Security Center. If you are using Kaspersky Security in multitenancy mode, to protect the virtual infrastructure of each tenant organization, you must map a virtual Administration Server to the vCloud Director organization containing the virtual machines of the tenant. The list of mappings is configured in the Integration Server Console.
During its operation, the Integration Server saves the following information:
- Integration Server connection settings, including passwords for Integration Server accounts
- Settings for connecting the Integration Server to VMware vCenter Server, VMware vCloud Director, and VMware NSX Manager
- SVM configuration settings, including passwords of the root user account and klconfig user account used on SVMs
- List of protected virtual machines, including the time of last events that occurred during protection and scanning of file system objects and during scanning of network traffic and web addresses
All data except the list of protected virtual machines is securely stored. Information is stored on the computer on which Integration Server is installed and is not sent to Kaspersky.
Page topAbout Integration Server Console
The Integration Server Console contains the following sections:
Integration Server settings section
In this section, you can view information about the Integration Server.
Integration Server user accounts section
In this section, you can change the passwords of accounts that are used to connect to the Integration Server.
The Virtual infrastructure protection section.
This section opens by default after the Integration Server Console is started. In this section, you can configure the connection of the Integration Server to virtual infrastructure administration servers (VMware vCenter Server and VMware vCloud Director), define or change the settings for registering and deploying Kaspersky Security services, or unregister Kaspersky Security services.
The table displays all virtual infrastructure administration servers (VMware vCenter Server and VMware vCloud Director) for which a connection is configured for the Integration Server.
The following buttons are provided above the table:
- The Add button opens the Connection to virtual infrastructure window. In this window, you can select the type of virtual infrastructure administration servers to which you need to configure a connection, and enter the settings for connecting to the VMware vCenter Server or VMware vCloud Director: IP address in IPv4 format or fully qualified domain name (FQDN), name and password of the account used by the Integration Server to connect to the server.
- The Refresh button lets you update the status of interaction between the Integration Server and the virtual infrastructure.
For each VMware vCenter Server, the following information is displayed in the table:
- IP address in IPv4 format or fully qualified domain name (FQDN) of the VMware vCenter Server.
- Group of settings containing connection error messages (if any) and a list of actions that you can perform when configuring the connection to this VMware vCenter Server and for subsequent deployment of protection of the virtual infrastructure managed by this VMware vCenter Server. You can expand or collapse the list of possible actions for each VMware vCenter Server by clicking on the address or name of the server.
- Information about deployment of protection on VMware clusters managed by this VMware vCenter Server, presented in the format
N/M, where:- N is the number of VMware ESXi hypervisors on which the file system protection service (Kaspersky File Antimalware Protection) is deployed, or a dash if the service is not registered in VMware NSX Manager.
- M is the number of VMware ESXi hypervisors on which the network protection service (Kaspersky Network Protection) is deployed, or a dash if the service is not registered in VMware NSX Manager.
The total number of VMware ESXi hypervisors managed by this VMware vCenter Server is indicated in parentheses.
The table displays the following information for each VMware vCloud Director Server:
- IP address in IPv4 format or fully qualified domain name (FQDN) of the VMware vCloud Director server.
- Group of settings containing connection error messages (if any) and a list of actions that you can perform when configuring the connection to this VMware vCloud Director and for subsequent deployment of protection of the virtual infrastructure managed by this VMware vCloud Director. You can expand or collapse the list of possible actions for each VMware vCloud Director server by clicking on the address or name of the server.
If no connection could be established with the VMware vCenter Server, VMware vCloud Director, or VMware NSX Manager, the table shows a warning.
If a connection error occurs because the certificate received from the VMware vCenter Server, VMware vCloud Director, or VMware NSX Manager is not trusted for the Integration Server, but the received certificate complies with the security policy of your organization, you can confirm the authenticity of the certificate and establish a connection. To do so, click the link in the problem description to open the Certificate validation window and click the Install certificate button. The received certificate is saved as a trusted certificate for the Integration Server.
Certificates that are trusted in the operating system in which the Integration Server is installed are also considered to be trusted for the Integration Server.
If there are problems with the SSL certificate, it is recommended to make sure that the utilized data transfer channel is secure.
The table also displays a warning if redirection of traffic to the network protection service (Kaspersky Network Protection) is disabled in one or more NSX security policies that are configured to use Kaspersky Security services. If you want to protect virtual machines against network threats, you need to enable redirection of traffic to the network protection service in NSX security policies (Redirect to service setting).
List of possible actions for the VMware vCenter Server:
- Register Kaspersky Security services – starts the Wizard that lets you enter the settings necessary for registering Kaspersky Security services in VMware NSX Manager and deploying those services on VMware clusters, and for configuring new SVMs. When you have finished entering the settings, Integration Server registers the Kaspersky Security services in VMware NSX Manager.
- Change settings of Kaspersky Security – starts the Wizard that lets you change the connection settings for interaction between the Integration Server and VMware NSX Manager, specify or change SVM images for the file system protection service (Kaspersky File Antimalware Protection) and/or the network protection service (Kaspersky Network Protection), and change the SVM configuration settings that are applied on new SVMs and on previously deployed SVMs. When you have finished entering the settings, the Integration Server applies the new settings and, if necessary, re-registers the Kaspersky Security services in VMware NSX Manager.
- Unregister Kaspersky Security services – opens a window in which you can specify the Kaspersky Security service that you need to unregister in VMware NSX Manager. You can unregister one or both Kaspersky Security services. Unregistration is performed by the Integration Server.
Kaspersky Security services can be unregistered only if all SVMs have been removed from VMware clusters and services are not being used in NSX Security Policies. Removal of SVMs and configuration of NSX Security Policies is performed in the VMware vSphere Web Client console.
- Change VMware vCenter Server connection settings – opens the Connection to virtual infrastructure window in which you can change the settings for connecting the Integration Server to a VMware vCenter Server.
- Remove VMware vCenter Server from the list – opens a window in which you can confirm deletion of the settings for connecting the Integration Server to this VMware vCenter Server. The VMware vCenter Server will be removed from the list of virtual infrastructure administration servers to which the Integration Server connects.
Removing a VMware vCenter Server from the list is possible only if Kaspersky Security services are not registered in VMware NSX Manager.
List of available actions for VMware vCloud Director:
- Map vCloud Director organizations – opens the vCloud Director organizations to virtual administration Servers mapping list window in which you can map vCloud Director organizations containing virtual machines of tenants to virtual Administration Servers of Kaspersky Security Center.
- Change VMware vCloud Director connection settings – opens the Connection to virtual infrastructure window in which you can change the settings for connecting the Integration Server to VMware vCloud Director.
- Remove VMware vCloud Director from list – opens a window in which you can confirm deletion of the settings for connecting the Integration Server to this VMware vCloud Director. The VMware vCloud Director Server will be removed from the list of virtual infrastructure administration servers to which the Integration Server connects.
Manage protection of tenant organizations section
This section is used only if the application is operating in multitenancy mode.
In this section, you can do the following:
- Connect the Integration Server to the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server.
The Integration Server connects to the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server to receive information about virtual Administration Servers created in Kaspersky Security Center, and to map virtual Administration Servers to vCloud Director organizations that contain virtual machines of tenants.
- View or configure the list of mappings between vCloud Director organizations containing virtual machines of tenants and virtual Administration Servers of Kaspersky Security Center.
A vCloud Director organization must be mapped to a virtual Administration Server so that Kaspersky Security can be used to protect virtual machines that are part of the vCloud Director organization.
About data processing
During their operation, Kaspersky Security components may save and send to other application components (and to Kaspersky Security Center) the following information that may contain personal data:
- To generate reports and events, SVMs send information about application operation to the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server. The transmitted information may include the names of processed files and paths to them in the file system, the names and addresses of virtual machines, and processed web addresses.
- To ensure the capability to work with Backup objects via Kaspersky Security Center, SVMs send the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server information about objects that have been placed in Backup. The transmitted information may include the object name and path to it in the file system. If requested by the administrator, the objects placed in Backup may also be sent to Kaspersky Security Center.
- While tasks are running, SVMs send information about task settings and results to the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server.
- SVMs send a list of protected virtual machines to the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server to be displayed in the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Console. The transmitted information may include the name of the protected virtual machine and the path to it in the virtual infrastructure.
- SVMs receive the policy-defined operating settings from the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server. The transmitted information may include file paths and web addresses.
- While SVMs are being configured, the Integration Server sends the SVMs the user-defined root and klconfig account passwords, the network data storage connection settings for SVMs, the IP address of the Integration Server, and the settings for connecting to the Integration Server and to the Kaspersky Security Center Administration Server.
- To support the operation of the application, the Integration Server receives information about the virtual infrastructure from the VMware vCenter Server and sends that information to SVMs.
The specified information is transmitted over encrypted data channels.
Page top