Contents
- Connector settings
- Connector, internal type
- Connector, tcp type
- Connector, udp type
- Connector, netflow type
- Connector, sflow type
- Connector, nats-jetstream type
- Connector, kafka type
- Connector, http type
- Connector, sql type
- Connector, file type
- Connector, 1c-log type
- Connector, 1c-xml type
- Connector, diode type
- Connector, ftp type
- Connector, nfs type
- Connector, wmi type
- Connector, wec type
- Connector, etw type
- Connector, snmp type
- Connector, snmp-trap type
- Connector, kata/edr type
- Connector, vmware type
- Connector, elastic type
- Connector, office365 type
Connector settings
This section describes the settings of all connector types supported by KUMA.
Connector, internal type
Connectors of the internal type are used for receiving data from KUMA services using the 'internal' protocol. For example, you must use such a connector to receive the following data:
- Internal data, such as event routes.
- File attributes. If while creating the collector at the Transport step of the installation wizard, you specified a connector of the file, 1c-xml, or 1c-log type, at the Event parsing step, in the Mapping table, you can pass the name of the file being processed by the collector or the path to the file in the KUMA event field. To do this, in the Source column, specify one of the following values:
$kuma_fileSourceNameto pass the name of the file being processed by the collector in the KUMA event field.$kuma_fileSourcePathto pass the path to the file being processed by the collector in the KUMA event field.
When you use a file, 1c-xml, or 1c-log connector, the new variables in the normalizer will only work with destinations of the internal type.
- Events to the event router. The event router can only receive events over the 'internal' protocol, therefore you can only use internal destinations when sending events to the event router.
Settings for a connector of the internal type are described in the following tables.
Basic settings tab
Setting |
Description |
|---|---|
Name |
Unique name of the resource. The maximum length of the name is 128 Unicode characters. Required setting. |
Tenant |
The name of the tenant that owns the resource. Required setting. |
Type |
Connector type: internal. Required setting. |
Tags |
Tags for resource search. Optional setting. |
URL |
The URL and port that the connector is listening on. You can enter a value in one of the following formats:
You can specify IPv6 addresses in the following format: You can add multiple values or delete values. To add a value, click the + Add button. To delete a value, click the delete Required setting. |
Description |
Description of the resource. The maximum length of the description is 4000 Unicode characters. |
Advanced settings tab
Setting |
Description |
|---|---|
Debug |
The switch enables resource logging. The toggle switch is turned off by default. |
Connector, tcp type
Connectors of the tcp type are used for passively receiving events over TCP when working with Windows and Linux agents. Settings for a connector of the tcp type are described in the following tables.
Basic settings tab
Setting |
Description |
|---|---|
Name |
Unique name of the resource. The maximum length of the name is 128 Unicode characters. Required setting. |
Tenant |
The name of the tenant that owns the resource. Required setting. |
Type |
Connector type: tcp. Required setting. |
Tags |
Tags for resource search. Optional setting. |
URL |
URL that you want to connect to. You can enter a URL in one of the following formats:
Required setting. |
Auditd |
This toggle switch enables the auditd mechanism to group auditd event lines received from the connector into an auditd event. If you enable this toggle switch, you cannot select a value in the Delimiter drop-down list because \n is automatically selected for the auditd mechanism. If you enable this toggle switch in the connector settings of the agent, you need to select \n in the Delimiter drop-down list in the connector settings of the collector to which the agent sends events. The maximum size of a grouped auditd event is approximately 4,174,304 characters. KUMA classifies Auditd events in accordance with the algorithm. For example, suppose the following records were received for processing:
The algorithm gives one single-line event of the LOGIN type (because the LOGIN type has code 1006 and it is less than 1300, which is the code of AUDIT_FIRST_EVENT), and one multi-line event with SYSCALL and PROCTITLE. |
Delimiter |
The character that marks the boundary between events:
If you do not select a value in this drop-down list, \n is selected by default. |
Description |
Description of the resource. The maximum length of the description is 4000 Unicode characters. |
Advanced settings tab
Setting |
Description |
|---|---|
Debug |
The switch enables resource logging. The toggle switch is turned off by default. |
Buffer size |
Buffer size in bytes for accumulating events in the RAM of the server before sending them for further processing or storage. The value must be a positive integer. Default buffer size: 1,048,576 bytes (1 MB). Maximum buffer size: 67,108,864 bytes (64 MB). |
Character encoding |
Character encoding. The default is UTF-8. |
Event buffer TTL |
Buffer lifetime for auditd event lines, in milliseconds. Auditd event lines enter the KUMA collector and accumulate in the buffer. This allows multiple auditd event lines to be grouped into a single auditd event. The buffer lifetime countdown begins when the first auditd event line is received or when the previous buffer lifetime expires. Possible values: from 50 to 30,000. The default value is This field is available if you have enabled the Auditd toggle switch on the Basic settings tab. The auditd event lines accumulated in the buffer are kept in the RAM of the server. We recommend caution when increasing the buffer size because memory usage by the KUMA collector may become excessive. You can verify how much server RAM the KUMA collector is using in KUMA metrics. If you want a buffer lifetime to exceed 30,000 milliseconds, we recommend using a different auditd event transport. For example, you can use an agent or pre-accumulate auditd events in a file, and then process this file with the KUMA collector. |
Transport header |
Regular expression for auditd events, which is used to identify auditd event lines. You can use the default value or edit it. The regular expression must contain the You can revert to the default regular expression for auditd events by clicking Reset to default value. |
TLS mode |
TLS encryption mode. When using TLS encryption, you cannot specify an IP address in the URL field on the Basic settings tab. Available values:
|
Compression |
Drop-down list for configuring Snappy compression:
|
Connector, udp type
Connectors of the udp type are used for passively receiving events over UDP when working with Windows and Linux agents. Settings for a connector of the udp type are described in the following tables.
Basic settings tab
Setting |
Description |
|---|---|
Name |
Unique name of the resource. The maximum length of the name is 128 Unicode characters. Required setting. |
Tenant |
The name of the tenant that owns the resource. Required setting. |
Type |
Connector type: udp. Required setting. |
URL |
URL that you want to connect to. You can enter a URL in one of the following formats:
Required setting. |
Auditd |
This toggle switch enables the auditd mechanism to group auditd event lines received from the connector into an auditd event. If you enable this toggle switch, you cannot select a value in the Delimiter drop-down list because \n is automatically selected for the auditd mechanism. If you enable this toggle switch in the connector settings of the agent, you need to select \n in the Delimiter drop-down list in the connector settings of the collector to which the agent sends events. The maximum size of a grouped auditd event is approximately 4,174,304 characters. KUMA classifies Auditd events in accordance with the algorithm. For example, suppose the following records were received for processing:
The algorithm gives one single-line event of the LOGIN type (because the LOGIN type has code 1006 and it is less than 1300, which is the code of AUDIT_FIRST_EVENT), and one multi-line event with SYSCALL and PROCTITLE. |
Delimiter |
The character that marks the boundary between events:
If you do not select a value in this drop-down list, \n is selected by default. |
Description |
Description of the resource. The maximum length of the description is 4000 Unicode characters. |
Advanced settings tab
Setting |
Description |
|---|---|
Debug |
The switch enables resource logging. The toggle switch is turned off by default. |
Buffer size |
Buffer size in bytes for accumulating events in the RAM of the server before sending them for further processing or storage. The value must be a positive integer. Default buffer size: 1,048,576 bytes (1 MB). Maximum buffer size: 67,108,864 bytes (64 MB). |
Number of handlers |
Number of handlers that the service can run simultaneously to process response rules in parallel. To determine the number of handlers, you can use the following formula: (<number of CPUs> / 2) + 2. The value must be a positive integer up to 999. |
Character encoding |
Character encoding. The default is UTF-8. |
Event buffer TTL |
Buffer lifetime for auditd event lines, in milliseconds. Auditd event lines enter the KUMA collector and accumulate in the buffer. This allows multiple auditd event lines to be grouped into a single auditd event. The buffer lifetime countdown begins when the first auditd event line is received or when the previous buffer lifetime expires. Possible values: from 50 to 30,000. The default value is This field is available if you have enabled the Auditd toggle switch on the Basic settings tab. The auditd event lines accumulated in the buffer are kept in the RAM of the server. We recommend caution when increasing the buffer size because memory usage by the KUMA collector may become excessive. You can verify how much server RAM the KUMA collector is using in KUMA metrics. If you want a buffer lifetime to exceed 30,000 milliseconds, we recommend using a different auditd event transport. For example, you can use an agent or pre-accumulate auditd events in a file, and then process this file with the KUMA collector. |
Transport header |
Regular expression for auditd events, which is used to identify auditd event lines. You can use the default value or edit it. The regular expression must contain the You can revert to the default regular expression for auditd events by clicking Reset to default value. |
Compression |
Drop-down list for configuring Snappy compression:
|
Connector, netflow type
Connectors of the netflow type are used for passively receiving events in the NetFlow format. Settings for a connector of the netflow type are described in the following tables.
Basic settings tab
Setting |
Description |
|---|---|
Name |
Unique name of the resource. The maximum length of the name is 128 Unicode characters. Required setting. |
Tenant |
The name of the tenant that owns the resource. Required setting. |
Type |
Connector type: netflow. Required setting. |
Tags |
Tags for resource search. Optional setting. |
URL |
URL that you want to connect to. The following URL formats are supported:
You can add multiple URLs or remove an URL. KUMA does not allow saving a resource or service if the URL field contains a tab or space character. To add an URL, click the + Add button. To remove an URL, click the delete Required setting. |
Description |
Description of the resource. The maximum length of the description is 4000 Unicode characters. |
Advanced settings tab
Setting |
Description |
|---|---|
Debug |
The switch enables resource logging. The toggle switch is turned off by default. |
Buffer size |
Buffer size in bytes for accumulating events in the RAM of the server before sending them for further processing or storage. The value must be a positive integer. Default buffer size: 1,048,576 bytes (1 MB). Maximum buffer size: 67,108,864 bytes (64 MB). |
Number of handlers |
Number of handlers that the service can run simultaneously to process response rules in parallel. To determine the number of handlers, you can use the following formula: (<number of CPUs> / 2) + 2. The value must be a positive integer up to 999. |
Character encoding |
Character encoding. The default is UTF-8. |
Connector, sflow type
Connectors of the sflow type are used for passively receiving events in the sFlow format. For sFlow, only structures described in sFlow version 5 are supported. Settings for a connector of the sflow type are described in the following tables.
Basic settings tab
Setting |
Description |
|---|---|
Name |
Unique name of the resource. The maximum length of the name is 128 Unicode characters. Required setting. |
Tenant |
The name of the tenant that owns the resource. Required setting. |
Type |
Connector type: sflow. Required setting. |
URL |
URL that you want to connect to. You can enter a URL in one of the following formats:
Required setting. |
Description |
Description of the resource. The maximum length of the description is 4000 Unicode characters. |
Advanced settings tab
Setting |
Description |
|---|---|
Debug |
The switch enables resource logging. The toggle switch is turned off by default. |
Buffer size |
Buffer size in bytes for accumulating events in the RAM of the server before sending them for further processing or storage. The value must be a positive integer. Default buffer size: 1,048,576 bytes (1 MB). Maximum buffer size: 67,108,864 bytes (64 MB). |
Number of handlers |
Number of handlers that the service can run simultaneously to process response rules in parallel. To determine the number of handlers, you can use the following formula: (<number of CPUs> / 2) + 2. The value must be a positive integer up to 999. |
Character encoding |
Character encoding. The default is UTF-8. |
Connector, nats-jetstream type
Connectors of the nats-jetstream type are used for interacting with a NATS message broker when working with Windows and Linux agents. Settings for a connector of the nats-jetstream type are described in the following tables.
Basic settings tab
Setting |
Description |
|---|---|
Name |
Unique name of the resource. The maximum length of the name is 128 Unicode characters. Required setting. |
Tenant |
The name of the tenant that owns the resource. Required setting. |
Type |
Connector type: nats-jetstream. Required setting. |
Tags |
Tags for resource search. Optional setting. |
URL |
URL that you want to connect to. The following URL formats are supported:
You can add multiple URLs or remove an URL. KUMA does not allow saving a resource or service if the URL field contains a tab or space character. To add an URL, click the + Add button. To remove an URL, click the delete Required setting. |
Authorization |
Type of authorization when connecting to the URL specified in the URL field:
|
Subject |
The topic of NATS messages. Characters are entered in Unicode encoding. Required setting. |
GroupID. |
The value of the |
Delimiter |
The character that marks the boundary between events:
If you do not select a value in this drop-down list, \n is selected by default. |
Description |
Description of the resource. The maximum length of the description is 4000 Unicode characters. |
Advanced settings tab
Setting |
Description |
|---|---|
Debug |
The switch enables resource logging. The toggle switch is turned off by default. |
Buffer size |
Buffer size in bytes for accumulating events in the RAM of the server before sending them for further processing or storage. The value must be a positive integer. Default buffer size: 1,048,576 bytes (1 MB). Maximum buffer size: 67,108,864 bytes (64 MB). |
Number of handlers |
Number of handlers that the service can run simultaneously to process response rules in parallel. To determine the number of handlers, you can use the following formula: (<number of CPUs> / 2) + 2. The value must be a positive integer up to 999. |
Character encoding |
Character encoding. The default is UTF-8. |
TLS mode |
TLS encryption mode. When using TLS encryption, you cannot specify an IP address in the URL field on the Basic settings. Available values:
|
Compression |
Drop-down list for configuring Snappy compression:
|
Connector, kafka type
Connectors of the kafka type are used for communicating with the Apache Kafka data bus when working with Windows and Linux agents. Settings for a connector of the kafka type are described in the following tables.
Basic settings tab
Setting |
Description |
|---|---|
Name |
Unique name of the resource. The maximum length of the name is 128 Unicode characters. Required setting. |
Tenant |
The name of the tenant that owns the resource. Required setting. |
Type |
Connector type: kafka. Required setting. |
Tags |
Tags for resource search. Optional setting. |
URL |
URL that you want to connect to. The following URL formats are supported:
You can add multiple URLs or remove an URL. KUMA does not allow saving a resource or service if the URL field contains a tab or space character. To add an URL, click the + Add button. To remove an URL, click the delete Required setting. |
Authorization |
Type of authorization when connecting to the URL specified in the URL field:
|
Topic |
Subject of Kafka messages. The maximum length of the subject is 255 characters. Space and tab characters are not allowed. You can use the following characters: a–z, A–Z, 0–9, ".", "_", "-". Required setting. |
GroupID. |
The value of the |
Delimiter |
The character that marks the boundary between events:
If you do not select a value in this drop-down list, \n is selected by default. |
Description |
Description of the resource. The maximum length of the description is 4000 Unicode characters. |
Advanced settings tab
Setting |
Description |
|---|---|
Debug |
The switch enables resource logging. The toggle switch is turned off by default. |
Number of handlers |
Number of handlers that the service can run simultaneously to process response rules in parallel. To determine the number of handlers, you can use the following formula: (<number of CPUs> / 2) + 2. The value must be a positive integer up to 999. |
Character encoding |
Character encoding. The default is UTF-8. |
TLS mode |
TLS encryption mode. When using TLS encryption, you cannot specify an IP address in the URL field on the Basic settings. Available values:
|
Size of message to fetch |
Size of one message in the request, in bytes. The default value of 16 MB is applied if no value is specified or 0 is specified. It cannot exceed 2147483647 bytes. |
Maximum fetch wait time |
Timeout for one message in seconds. The default value of 5 seconds is applied if no value is specified or 0 is specified. Maximum possible value: 2147483647. |
Connection timeout |
Kafka broker connection timeout in seconds. Maximum possible value: 2147483647. The default value is 30 seconds. |
Read timeout |
Read operation timeout in seconds. Maximum possible value: 2147483647. The default value is 30 seconds. |
Write timeout |
Write operation timeout in seconds. Maximum possible value: 2147483647. The default value is 30 seconds. |
Group status update interval |
Group status update interval in seconds Cannot exceed session time. The recommended value is 1/3 of the session time. Maximum possible value: 2147483647. The default value is 30 seconds. |
Session time |
Session time in seconds. Maximum possible value: 2147483647. The default value is 30 seconds. |
Maximum time to process one message |
Maximum time to process one message by a single thread, in milliseconds. Maximum possible value: 2147483647. The default value is 100 milliseconds. |
Enable autocommit |
Enabled by default. |
Autocommit interval |
Autocommit interval in seconds The default value is 1 second. Maximum possible value: 18446744073709551615. Any positive number can be specified. |
PFX secret |
Secret of the pfx type. This field is available if Authorization is set to PFX. You can select an existing secret or create a new secret. To create a new secret, select Create new. Required field. |
Secret |
Secret of the 'credentials' type. This field is available if Authorization is set to Plain. You can select an existing secret or create a new secret. To create a new secret, select Create new. Required field. |
Connector, http type
Connectors of the http type are used for receiving events over HTTP when working with Windows and Linux agents. Settings for a connector of the http type are described in the following tables.
Basic settings tab
Setting |
Description |
|---|---|
Name |
Unique name of the resource. The maximum length of the name is 128 Unicode characters. Required setting. |
Tenant |
The name of the tenant that owns the resource. Required setting. |
Type |
Connector type: http. Required setting. |
Tags |
Tags for resource search. Optional setting. |
URL |
URL that you want to connect to. You can enter a URL in one of the following formats:
Required setting. |
Delimiter |
The character that marks the boundary between events:
If you do not select a value in this drop-down list, \n is selected by default. |
Description |
Description of the resource. The maximum length of the description is 4000 Unicode characters. |
Advanced settings tab
Setting |
Description |
|---|---|
Debug |
The switch enables resource logging. The toggle switch is turned off by default. |
Character encoding |
Character encoding. The default is UTF-8. |
TLS mode |
TLS encryption mode. When using TLS encryption, you cannot specify an IP address in the URL field on the Basic settings tab. Available values:
|
Connector, sql type
Connectors of the sql type are used for querying databases. KUMA supports multiple types of databases. When creating a connector of the sql type, you must specify general connector settings and individual database connection settings. Settings for a connector of the sql type are described in the following tables.
Basic settings tab
Setting |
Description |
|---|---|
Name |
Unique name of the resource. The maximum length of the name is 128 Unicode characters. Required setting. |
Tenant |
The name of the tenant that owns the resource. Required setting. |
Type |
Connector type: sql. Required setting. |
Tags |
Tags for resource search. Optional setting. |
Default query |
SQL query that is executed when connecting to the database. Required setting. |
Reconnect to the database every time a query is sent |
This toggle enables reconnection of the connector to the database every time a query is sent. This toggle switch is turned off by default. |
Poll interval, sec |
Interval for executing SQL queries in seconds. The default value is 10 seconds. |
Connection |
Database connection settings:
You can add multiple connections or delete a connection. To add a connection, click the + Add connection button. To remove a connection, click the delete |
Description |
Description of the resource. The maximum length of the description is 4000 Unicode characters. |
Advanced settings tab
Setting |
Description |
|---|---|
Debug |
The switch enables resource logging. The toggle switch is turned off by default. |
Character encoding |
Character encoding. The default is UTF-8. KUMA converts SQL responses to UTF-8 encoding. You can configure the SQL server to send responses in UTF-8 encoding or change the encoding of incoming messages on the KUMA side. |
Within a single connector, you can create a connection for multiple supported databases. If a collector with a connector of the sql type cannot be started, check if the /opt/kaspersky/kuma/collector/<collector ID>/sql/state-<file ID> state file is empty. If the state file is empty, delete it and restart the collector.
Supported SQL types and their specific usage features
The following SQL types are supported:
- MSSQL.
For example:
sqlserver://{user}:{password}@{server:port}/{instance_name}?database={database}
We recommend using this URL variant.
sqlserver://{user}:{password}@{server}?database={database}
The characters
@p1are used as a placeholder in the SQL query.If you want to connect using domain account credentials, specify the account name in
<domain>%5C<user>format. For example:sqlserver://domain%5Cuser:password@ksc.example.com:1433/SQLEXPRESS?database=KAV. - MySQL/MariaDB
For example:
mysql://{user}:{password}@tcp({server}:{port})/{database}The characters
?are used as placeholders in the SQL query. - PostgreSQL.
For example:
postgres://{user}:{password}@{server}/{database}?sslmode=disableThe characters
$1are used as a placeholder in the SQL query. - CockroachDB
For example:
postgres://{user}:{password}@{server}:{port}/{database}?sslmode=disableThe characters
$1are used as a placeholder in the SQL query. - SQLite3
For example:
sqlite3://file:{file_path}A question mark (
?) is used as a placeholder in the SQL query.When querying SQLite3, if the initial value of the ID is in datetime format, you must add a date conversion with the
sqlite datetimefunction to the SQL query. For example:select * from connections where datetime(login_time) > datetime(?, 'utc') order by login_timeIn this example,
connectionsis the SQLite table, and the value of the variable?is taken from the Identity seed field, and it must be specified in the{<date>}T{<time>}Zformat, for example,2021-01-01T00:10:00Z). - Oracle DB
Example URL of a secret with the 'oracle' driver:
oracle://{user}:{password}@{server}:{port}/{service_name}oracle://{user}:{password}@{server}:{port}/?SID={SID_VALUE}If the query execution time exceeds 30 seconds, the oracle driver aborts the SQL request, and the following error appears in the collector log: user requested cancel of current operation. To increase the execution time of an SQL query, specify the value of the timeout parameter in seconds in the connection string, for example:
oracle://{user}:{password}@{server}:{port}/{service_name}?timeout=300The
:valvariable is used as a placeholder in the SQL query.When querying Oracle DB, if the identity seed is in the datetime format, you must consider the type of the field in the database and, if necessary, add conversions of the time string in the SQL query to make sure the SQL connector works correctly. For example, if the
Connectionstable in the database has alogin_timefield, the following conversions are possible:- If the login_time field has the TIMESTAMP type, then depending on the configuration of the database, the login_time field may contain a value in the
YYYY-MM-DD HH24:MI:SSformat, for example,2021-01-01 00:00:00. In this case, you need to specify2021-01-01T00:00:00Zin the Identity seed field, and in the SQL query, perform the conversion using theto_timestampfunction, for example:select * from connections where login_time > to_timestamp(:val, 'YYYY-MM-DD"T"HH24:MI:SS"Z"') - If the login_time field has the TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE type, then depending on the configuration of the database, the login_time field may contain a value in the
YYYY-MM-DD"T"HH24:MI:SSTZH:TZMformat (for example,2021-01-01T00:00:00+03:00). In this case, you need to specify2021-01-01T00:00:00+03:00in the Identity seed field, and in the SQL query, perform the conversion using theto_timestamp_tzfunction, for example:select * from connections_tz where login_time > to_timestamp_tz(:val, 'YYYY-MM-DD"T"HH24:MI:SSTZH:TZM')For details about the
to_timestampandto_timestamp_tzfunctions, please refer to the official Oracle documentation.
To interact with Oracle DB, you must install the libaio1 Astra Linux package.
- If the login_time field has the TIMESTAMP type, then depending on the configuration of the database, the login_time field may contain a value in the
- Firebird SQL
For example:
firebirdsql://{user}:{password}@{server}:{port}/{database}A question mark (
?) is used as a placeholder in the SQL query.If a problem occurs when connecting Firebird on Windows, use the full path to the database file, for example:
firebirdsql://{user}:{password}@{server}:{port}/C:\Users\user\firebird\db.FDB - ClickHouse
For example:
clickhouse://{user}:{password}@{server}:{port}/{database}A question mark (
?) is used as a placeholder in the SQL query.KUMA supports the following data types:
- Data that can be cast to string (such as strings, numeric values, and BLOBs) is displayed as strings.
- Arrays and maps are displayed in JSON format or using the built-in
go fmt.Sprintf("%v",v)function to display them in the best possible way.
Two methods of connecting to ClickHouse are possible:
- Without credentials, by entering a URL:
clickhouse://host:port/database - With credentials, by entering a URL:
clickhouse://user:password@host:port/database
When using TLS encryption, by default, the connector works only on port 9440. If TLS encryption is not used, by default, the connector works with ClickHouse only on port 9000.
The connector does not work over HTTP.
If TLS encryption mode is configured on the ClickHouse server, and in connector settings, in the TLS mode drop-down list, you have selected Disabled or vice versa, the database connection cannot be established.
The TLS mode is used only if the ClickHouse driver is specified.
If you want to connect to the KUMA ClickHouse, in the SQL connector settings, specify the PublicPKI secret type, which contains the base64-encoded PEM private key and the public key.
In the parameters of the SQL connector for the ClickHouse connection type, you need to select Disabled in the TLS mode drop-down list. This value must not be specified if a certificate is used for authentication. If in the TLS mode drop-down list, you select Custom CA, you need to specify the ID of a secret of the 'certificate' type in the Identity column field. You also need to select one of the following values in the Authorization type drop-down list:
- Disabled. If you select this value, you need to leave the Identity column field blank.
- Plain. Select this value if the Secret separately check box is selected and the ID of a secret of the 'credentials' type is specified in the Identity column field.
- PublicPKI. Select this value if the Secret separately check box is selected and the ID of a secret of the PublicPKI type is specified in the Identity column field.
If the initial value of the ID contains an indication of time (
datetime), in the query, you must use a variable for time conversion (parseDateTimeBestEffort). For example, if the time is specified as2021-01-01 00:10:00, the following query may be used:select connections, username, host, login_time from connections where login_time > parseDateTimeBestEffort(?) order by login_time
A sequential request for database information is supported in SQL queries. For example, if in the Query field, you enter select * from <name of data table> where id > <placeholder>, the value of the Identity seed field is used as the placeholder value the first time you query the table. In addition, the service that utilizes the SQL connector saves the ID of the last read entry, and the ID of this entry will be used as the placeholder value in the next query to the database.
We recommend adding the order by command to the query string, followed by the sorting field. For example, select * from table_name where id > ? order by id.
Connector, file type
Connectors of the file type are used for getting data from text files when working with Windows and Linux agents. One line of a text file is considered to be one event. \n is used as the newline character.
If while creating the collector at the Transport step of the installation wizard, you specified a connector of the file type, at the Event parsing in the Mapping table, you can pass the name of the file being processed by the collector or the path to the file in the KUMA event field. To do this, in the Source column, specify one of the following values:
$kuma_fileSourceNameto pass the name of the file being processed by the collector in the KUMA event field.$kuma_fileSourcePathto pass the path to the file being processed by the collector in the KUMA event field.
When you use a file connector, the new variables in the normalizer will only work with destinations of the internal type.
To read Windows files, you need to create a connector of the file type and manually install the agent on Windows. The Windows agent must not read its files in the folder where the agent is installed. The connector will work even with a FAT file system; if the disk is defragmented, the connector re-reads all files from scratch because all inodes of files are reset.
We do not recommend running the agent under an administrator account; read permissions for folders/files must be configured for the user account of the agent. We do not recommend installing the agent on important systems; it is preferable to send the logs and read them on dedicated hosts with the agent.
For each file that the connector of the file type interacts with, a state file (states.ini) is created with the offset, dev, inode, and filename parameters. The state file allows the connector, to resume reading from the position where the connector last stopped instead of starting over when rereading the file. Some special considerations are involved in rereading files:
- If the
inodeparameter in the state file changes, the connector rereads the corresponding file from the beginning. When the file is deleting and recreated, theinodesetting in the associated state file may remain unchanged. In this case, when rereading the file, the connector resumes reading in accordance with theoffsetparameter. - If the file has been truncated or its size has become smaller, the connector start reading from the beginning.
- If the file has been renamed, when rereading the file, the connector resumes reading from the position where the connector last stopped.
- If the directory with the file has been remounted, when rereading the file, the connector resumes reading from the position where the connector last stopped. You can specify the path to the files with which the connector interacts when configuring the connector in the File path field.
Settings for a connector of the file type are described in the following tables.
Basic settings tab
Setting |
Description |
|---|---|
Name |
Unique name of the resource. The maximum length of the name is 128 Unicode characters. Required setting. |
Tenant |
The name of the tenant that owns the resource. Required setting. |
Type |
Connector type: file. Required setting. |
Tags |
Tags for resource search. Optional setting. |
Path to the file. |
The full path to the file that the connector interacts with. For example,
File and folder mask templates Limitations when using prefixes in file paths Limiting the number of files for watching by mask Required setting. |
Update timeout, sec |
The time in seconds for which the file must not be updated for KUMA to apply the action specified in the Timeout action drop-down list to the file. Default value: The entered value must not be less than the value that you entered on the Advanced settings in the Poll interval, sec field. |
Timeout action |
The action that KUMA applies to the file after the time specified in the Update timeout, sec:
|
Auditd |
This toggle switch enables the auditd mechanism to group auditd event lines received from the connector into an auditd event. If you enable this toggle switch, you cannot select a value in the Delimiter drop-down list because \n is automatically selected for the auditd mechanism. If you enable this toggle switch in the connector settings of the agent, you need to select \n in the Delimiter drop-down list in the connector settings of the collector to which the agent sends events. The maximum size of a grouped auditd event is approximately 4,174,304 characters. KUMA classifies Auditd events in accordance with the algorithm. For example, suppose the following records were received for processing:
The algorithm gives one single-line event of the LOGIN type (because the LOGIN type has code 1006 and it is less than 1300, which is the code of AUDIT_FIRST_EVENT), and one multi-line event with SYSCALL and PROCTITLE. |
Description |
Description of the resource. The maximum length of the description is 4000 Unicode characters. |
Advanced settings tab
Setting |
Description |
|---|---|
Debug |
The switch enables resource logging. The toggle switch is turned off by default. |
Buffer size |
Buffer size in bytes for accumulating events in the RAM of the server before sending them for further processing or storage. The value must be a positive integer. Default buffer size: 1,048,576 bytes (1 MB). Maximum buffer size: 67,108,864 bytes (64 MB). |
Number of handlers |
Number of handlers that the service can run simultaneously to process response rules in parallel. To determine the number of handlers, you can use the following formula: (<number of CPUs> / 2) + 2. The value must be a positive integer up to 999. |
File/folder polling mode |
Specifies how the connector rereads files in the directory:
|
Poll interval, ms |
The interval in milliseconds at which the connector rereads files in the directory. Default value: The entered value must not be less than the value that you entered on the Basic settings in the Update timeout, sec field. We recommend entering a value less than the value that you entered in the Event buffer TTL field because this may adversely affect the performance of Auditd. |
Character encoding |
Character encoding. The default is UTF-8. |
Event buffer TTL |
Buffer lifetime for auditd event lines, in milliseconds. Auditd event lines enter the KUMA collector and accumulate in the buffer. This allows multiple auditd event lines to be grouped into a single auditd event. The buffer lifetime countdown begins when the first auditd event line is received or when the previous buffer lifetime expires. Possible values: 700 to 30,000. The default value is This field is available if you have enabled the Auditd toggle switch on the Basic settings tab. The auditd event lines accumulated in the buffer are kept in the RAM of the server. We recommend caution when increasing the buffer size because memory usage by the KUMA collector may become excessive. You can verify how much server RAM the KUMA collector is using in KUMA metrics. If you want a buffer lifetime to exceed 30,000 milliseconds, we recommend using a different auditd event transport. For example, you can use an agent or pre-accumulate auditd events in a file, and then process this file with the KUMA collector. |
Transport header |
Regular expression for auditd events, which is used to identify auditd event lines. You can use the default value or edit it. The regular expression must contain the You can revert to the default regular expression for auditd events by clicking Reset to default value. |
Connector, 1c-log type
Connectors of the 1c-log type are used for getting data from 1C technology logs when working with Linux agents. \n is used as the newline character. The connector accepts only the first line from a multi-line event record.
Settings for a connector of the 1c-log type are described in the following tables.
Basic settings tab
Setting |
Description |
|---|---|
Name |
Unique name of the resource. The maximum length of the name is 128 Unicode characters. Required setting. |
Tenant |
The name of the tenant that owns the resource. Required setting. |
Type |
Connector type: 1c-log. Required setting. |
Tags |
Tags for resource search. Optional setting. |
Directory path |
The full path to the directory with the files that you want to interact with, for example, Limitations when using prefixes in file paths Required setting. |
Description |
Description of the resource. The maximum length of the description is 4000 Unicode characters. |
Advanced settings tab
Setting |
Description |
|---|---|
Debug |
The switch enables resource logging. The toggle switch is turned off by default. |
Buffer size |
Buffer size in bytes for accumulating events in the RAM of the server before sending them for further processing or storage. The value must be a positive integer. Default buffer size: 1,048,576 bytes (1 MB). Maximum buffer size: 67,108,864 bytes (64 MB). |
File/folder polling mode |
Specifies how the connector rereads files in the directory:
|
Poll interval, ms |
The interval in milliseconds at which the connector rereads files in the directory. Default value: |
Character encoding |
Buffer size in bytes for accumulating events in the RAM of the server before sending them for further processing or storage. The value must be a positive integer. Default buffer size: 1,048,576 bytes (1 MB). Maximum buffer size: 67,108,864 bytes (64 MB). |
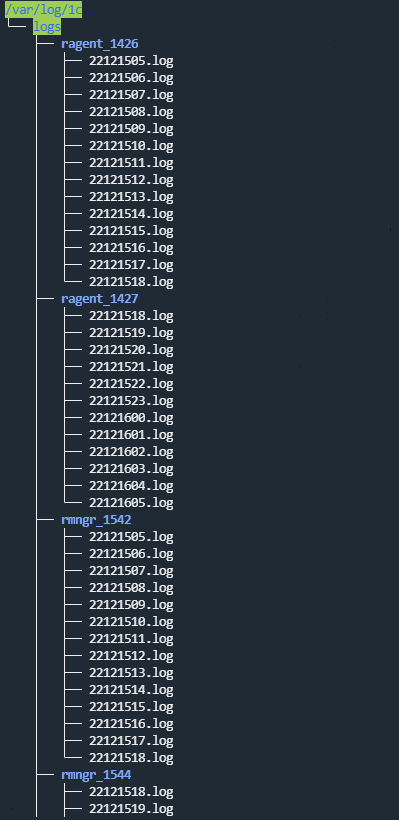
Connector operation diagram:
- All 1C technology log files are searched. Log file requirements:
- Files with the LOG extension are created in the log directory (
/var/log/1c/logs/by default) within a subdirectory for each process. - Events are logged to a file for an hour; after that, the next log file is created.
- The file names have the following format: <YY><MM><DD><HH>.log. For example, 22111418.log is a file created in 2022, in the 11th month, on the 14th at 18:00.
- Each event starts with the event time in the following format: <mm>:<ss>.<microseconds>-<duration in microseconds>.
- Files with the LOG extension are created in the log directory (
- The processed files are discarded. Information about processed files is stored in the file /<collector working directory>/1c_log_connector/state.json.
- Processing of the new events starts, and the event time is converted to the RFC3339 format.
- The next file in the queue is processed.
Connector limitations:
- Installation of a collector with a 1c-log connector is not supported in a Windows operating system. To set up transfer of 1C log files for processing by the KUMA collector:
- On the Windows server, grant read access over the network to the folder with the 1C log files.
- On the Linux server, mount the shared folder with the 1C log files on the Linux server (see the list of supported operating systems).
- On the Linux server, install the collector that you want to process 1C log files from the mounted shared folder.
- Only the first line from a multi-line event record is processed.
- The normalizer processes only the following types of events:
- ADMIN
- ATTN
- CALL
- CLSTR
- CONN
- DBMSSQL
- DBMSSQLCONN
- DBV8DBENG
- EXCP
- EXCPCNTX
- HASP
- LEAKS
- LIC
- MEM
- PROC
- SCALL
- SCOM
- SDBL
- SESN
- SINTEG
- SRVC
- TLOCK
- TTIMEOUT
- VRSREQUEST
- VRSRESPONSE
Connector, 1c-xml type
Connectors of the 1c-xml type are used for getting data from 1C registration logs when working with Linux agents. When the connector handles multi-line events, it converts them into single-line events.
Settings for a connector of the 1c-xml type are described in the following tables.
Basic settings tab
Setting |
Description |
|---|---|
Name |
Unique name of the resource. The maximum length of the name is 128 Unicode characters. Required setting. |
Tenant |
The name of the tenant that owns the resource. Required setting. |
Type |
Connector type: 1c-xml. Required setting. |
Tags |
Tags for resource search. Optional setting. |
Directory path |
The full path to the directory with the files that you want to interact with, for example, Limitations when using prefixes in file paths Required setting. |
Description |
Description of the resource. The maximum length of the description is 4000 Unicode characters. |
Advanced settings tab
Setting |
Description |
|---|---|
Debug |
The switch enables resource logging. The toggle switch is turned off by default. |
Buffer size |
Buffer size in bytes for accumulating events in the RAM of the server before sending them for further processing or storage. The value must be a positive integer. Default buffer size: 1,048,576 bytes (1 MB). Maximum buffer size: 67,108,864 bytes (64 MB). |
File/folder polling mode |
Specifies how the connector rereads files in the directory:
|
Poll interval, ms |
The interval in milliseconds at which the connector rereads files in the directory. Default value: |
Character encoding |
Character encoding. The default is UTF-8. |
Connector operation diagram:
- The files containing 1C logs with the XML extension are searched within the specified directory. Logs are placed in the directory either manually or using an application written in the 1C language, for example, using the
ВыгрузитьЖурналРегистрации()function. The connector only supports logs received this way. For more information on how to obtain 1C logs, see the official 1C documentation. - Files are sorted by the last modification time in ascending order. All the files modified before the last read are discarded.
Information about processed files is stored in the file /<collector working directory>/1c_xml_connector/state.ini and has the following format:
offset=<number>\ndev=<number>\ninode=<number>. - Events are defined in each unread file.
- Events from the file are processed one by one. Multi-line events are converted to single-line events.
Connector limitations:
- Installation of a collector with a 1c-xml connector is not supported in a Windows operating system. To set up transfer of 1C log files for processing by the KUMA collector:
- On the Windows server, grant read access over the network to the folder with the 1C log files.
- On the Linux server, mount the shared folder with the 1C log files on the Linux server (see the list of supported operating systems).
- On the Linux server, install the collector that you want to process 1C log files from the mounted shared folder.
- Files with an incorrect event format are not read. For example, if event tags in the file are in Russian, the collector does not read such events.
- If a file read by the connector is enriched with the new events and if this file is not the last file read in the directory, all events from the file are processed again.
Connector, diode type
Connectors of the diode type are used for unidirectional data transmission in industrial ICS networks using data diodes. Settings for a connector of the diode type are described in the following tables.
Basic settings tab
Setting |
Description |
|---|---|
Name |
Unique name of the resource. The maximum length of the name is 128 Unicode characters. Required setting. |
Tenant |
The name of the tenant that owns the resource. Required setting. |
Type |
Connector type: diode. Required setting. |
Tags |
Tags for resource search. Optional setting. |
Directory with events from the data diode |
Full path to the directory on the KUMA collector server, into which the data diode moves files with events from the isolated network segment. After the connector has read these files, the files are deleted from the directory. Maximum length of the path: 255 Unicode characters. Limitations when using prefixes in paths Required setting. |
Delimiter |
The character that marks the boundary between events:
If you do not select a value in this drop-down list, \n is selected by default. You must select the same value in the Delimiter drop-down list in the settings of the connector and the destination being used to transmit events from the isolated network segment using a data diode. |
Description |
Description of the resource. The maximum length of the description is 4000 Unicode characters. |
Advanced settings tab
Setting |
Description |
|---|---|
Debug |
The switch enables resource logging. The toggle switch is turned off by default. |
Number of handlers |
Number of handlers that the service can run simultaneously to process response rules in parallel. To determine the number of handlers, you can use the following formula: (<number of CPUs> / 2) + 2. The value must be a positive integer up to 999. |
Poll interval, sec |
Interval at which the files are read from the directory containing events from the data diode. The default value is 2 seconds. |
Character encoding |
Character encoding. The default is UTF-8. |
Compression |
Drop-down list for configuring Snappy compression:
You must select the same value in the Snappy drop-down list in the settings of the connector and the destination being used to transmit events from the isolated network segment using a data diode. |
Connector, ftp type
Connectors of the ftp type are used for getting data over File Transfer Protocol (FTP) when working with Windows and Linux agents. Settings for a connector of the ftp type are described in the following tables.
Basic settings tab
Setting |
Description |
|---|---|
Name |
Unique name of the resource. The maximum length of the name is 128 Unicode characters. Required setting. |
Tenant |
The name of the tenant that owns the resource. Required setting. |
Type |
Connector type: ftp. Required setting. |
Tags |
Tags for resource search. Optional setting. |
URL |
URL of file or file mask that begins with the If the URL does not contain the port number of the FTP server, port Required setting. |
Secret |
|
Description |
Description of the resource. The maximum length of the description is 4000 Unicode characters. |
Advanced settings tab
Setting |
Description |
|---|---|
Debug |
The switch enables resource logging. The toggle switch is turned off by default. |
Character encoding |
Character encoding. The default is UTF-8. |
Connector, nfs type
Connectors of the nfs type are used for getting data over Network File System (NFS) when working with Windows and Linux agents. Settings for a connector of the nfs type are described in the following tables.
Basic settings tab
Setting |
Description |
|---|---|
Name |
Unique name of the resource. The maximum length of the name is 128 Unicode characters. Required setting. |
Tenant |
The name of the tenant that owns the resource. Required setting. |
Type |
Connector type: nfs. Required setting. |
Tags |
Tags for resource search. Optional setting. |
URL |
Path to the remote directory in the Required setting. |
File name mask |
A mask used to filter files containing events. The following wildcards are acceptable " |
Poll interval, sec |
Poll interval in seconds. The time interval after which files are re-read from the remote system. The default value is |
Description |
Description of the resource. The maximum length of the description is 4000 Unicode characters. |
Advanced settings tab
Setting |
Description |
|---|---|
Debug |
The switch enables resource logging. The toggle switch is turned off by default. |
Character encoding |
Character encoding. The default is UTF-8. |
Connector, wmi type
Connectors of the wmi type are used for getting data using Windows Management Instrumentation when working with Windows agents. Settings for a connector of the wmi type are described in the following tables.
Basic settings tab
Setting |
Description |
|---|---|
Name |
Unique name of the resource. The maximum length of the name is 128 Unicode characters. Required setting. |
Tenant |
The name of the tenant that owns the resource. Required setting. |
Type |
Connector type: wmi. Required setting. |
Tags |
Tags for resource search. Optional setting. |
Description |
Description of the resource. The maximum length of the description is 4000 Unicode characters. |
URL |
URL of the collector that you created to receive data using Windows Management Instrumentation, for example, When a collector is created, an agent is automatically created that will get data on the remote device and forward it to the collector service. If you know which server the collector service will be installed on, the URL is known in advance. You can enter the URL of the collector in the URL field after completing the installation wizard. To do so, you first need to copy the URL of the collector in the Resources → Active services section. Required setting. |
Default credentials |
No value. You need to specify credentials for connecting to hosts in the Remote hosts table. |
Remote hosts |
Settings of remote Windows devices to connect to.
You can add multiple remote Windows devices or remove a remote Windows device. To add a remote Windows device, click + Add. To remove a remote Windows device, select the check box next to it and click Delete. |
Advanced settings tab
Setting |
Description |
|---|---|
Debug |
The switch enables resource logging. The toggle switch is turned off by default. |
Character encoding |
Character encoding. The default is UTF-8. |
TLS mode |
TLS encryption mode. When using TLS encryption, you cannot specify an IP address in the URL field on the Basic settings. Available values:
|
Compression |
Drop-down list for configuring Snappy compression:
|
If you edit a connector of this type, the TLS mode and Compression settings are visible and available on the connector resource as well as the collector. If you are using a connector of this type on a collector, the values of TLS mode and Compression settings are sent to the destination of automatically created agents.
Receiving events from a remote device
Conditions for receiving events from a remote Windows device hosting a KUMA agent:
- To start the KUMA agent on the remote device, you must use an account with the “Log on as a service” permissions.
- To receive events from the KUMA agent, you must use an account with Event Log Readers permissions. For domain servers, one such user account can be created so that a group policy can be used to distribute its rights to read logs to all servers and workstations in the domain.
- TCP ports 135, 445, and 49152–65535 must be opened on the remote Windows devices.
- You must run the following services on the remote machines:
- Remote Procedure Call (RPC)
- RPC Endpoint Mapper
Connector, wec type
Connectors of the wec type are used for getting data using Windows Event Forwarding (WEF) and Windows Event Collector (WEC), or local operating system logs of a Windows host when working with Windows agents. Settings for a connector of the wec type are described in the following tables.
Basic settings tab
Setting |
Description |
|---|---|
Name |
Unique name of the resource. The maximum length of the name is 128 Unicode characters. Required setting. |
Tenant |
The name of the tenant that owns the resource. Required setting. |
Type |
Connector type: wec. Required setting. |
Tags |
Tags for resource search. Optional setting. |
URL |
URL of the collector that you created to receive data using Windows Event Collector, for example, When a collector is created, an agent is automatically created that will get data on the remote device and forward it to the collector service. If you know which server the collector service will be installed on, the URL is known in advance. You can enter the URL of the collector in the URL field after completing the installation wizard. To do so, you first need to copy the URL of the collector in the Resources → Active services section. Required setting. |
Windows logs |
The names of the Windows logs that you want to get. By default, this drop-down list includes only preconfigured logs, but you can add custom log to the list. To do so, enter the names of the custom logs in the Windows logs field, then press ENTER. KUMA service and resource configurations may require additional changes in order to process custom logs correctly. Preconfigured logs:
If the name of at least one log is specified incorrectly, the agent using the connector does not receive events from any log, even if the names of other logs are correct. |
Description |
Description of the resource. The maximum length of the description is 4000 Unicode characters. |
Advanced settings tab
Setting |
Description |
|---|---|
Debug |
The switch enables resource logging. The toggle switch is turned off by default. |
Character encoding |
Character encoding. The default is UTF-8. |
TLS mode |
TLS encryption mode. When using TLS encryption, you cannot specify an IP address in the URL field on the Basic settings. Available values:
|
Compression |
Drop-down list for configuring Snappy compression:
|
If you edit a connector of this type, the TLS mode and Compression settings are visible and available on the connector resource as well as the collector. If you are using a connector of this type on a collector, the values of TLS mode and Compression settings are sent to the destination of automatically created agents.
To start the KUMA agent on the remote device, you must use a service account with the “Log on as a service” permissions. To receive events from the operating system log, the service user account must also have Event Log Readers permissions.
You can create one user account with “Log on as a service” and “Event Log Readers” permissions, and then use a group policy to extend the rights of this account to read the logs to all servers and workstations in the domain.
We recommend that you disable interactive logon for the service account.
Page topConnector, etw type
Connectors of the etw type are used for getting extended logs of DNS servers. Settings for a connector of the etw type are described in the following tables.
Basic settings tab
Setting |
Description |
|---|---|
Name |
Unique name of the resource. The maximum length of the name is 128 Unicode characters. Required setting. |
Tenant |
The name of the tenant that owns the resource. Required setting. |
Type |
Connector type: etw. Required setting. |
Tags |
Tags for resource search. Optional setting. |
URL |
URL of the DNS server. Required setting. |
Session name |
Session name that corresponds to the ETW provider: Microsoft-Windows-DNSServer {EB79061A-A566-4698-9119-3ED2807060E7}. If in a connector of the etw type, the session name is specified incorrectly, an incorrect provider is specified in the session, or an incorrect method is specified for sending events (to send events correctly, on the Windows Server side, you must specify "Real time" or "File and Real time" mode), events will not arrive from the agent, an error will be recorded in the agent log on Windows, and the status of the agent will be green. At the same time, no attempt will be made to get events every 60 seconds. If you modify session settings on the Windows side, you must restart the etw agent and/or the session for the changes to take effect. For details about specifying session settings on the Windows side to receive DNS server events, see the Configuring receipt of DNS server events using the ETW agent section. Required setting. |
Extract event information |
This toggle switch enables the extraction of the minimum set of event information that can be obtained without having to download third-party metadata from the disk. This method helps conserve CPU resources on the computer with the agent. By default, this toggle switch is enabled and all event data is extracted. |
Extract event properties |
This toggle switch enables the extraction of event properties. If this toggle switch is disabled, event properties are not extracted, which helps save CPU resources on the machine with the agent. By default, this toggle switch is enabled and event properties are extracted. You can enable the Extract event properties switch only if the Extract event information toggle switch is enabled. |
Description |
Description of the resource. The maximum length of the description is 4000 Unicode characters. |
Advanced settings tab
Setting |
Description |
|---|---|
Debug |
The switch enables resource logging. The toggle switch is turned off by default. |
Character encoding |
Character encoding. The default is UTF-8. |
TLS mode |
TLS encryption mode. When using TLS encryption, you cannot specify an IP address in the URL field on the Basic settings. Available values:
|
Compression |
Drop-down list for configuring Snappy compression:
|
If you edit a connector of this type, the TLS mode and Compression settings are visible and available on the connector resource as well as the collector. If you are using a connector of this type on a collector, the values of TLS mode and Compression settings are sent to the destination of automatically created agents.
Page topConnector, snmp type
Connectors of the snmp type are used for getting data over Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) when working with Windows and Linux agents. To process events received over SNMP, you must use the json normalizer. Supported SNMP protocol versions:
- snmpV1
- snmpV2
- snmpV3
Only one snmp connector created in the agent settings can be used in an agent. If you need to use multiple snmp connectors, you must create one or all snmp connectors as a separate resource and select it in the connection settings.
Available settings for a connector of the snmp type are described in the following tables.
Basic settings tab
Setting |
Description |
|---|---|
Name |
Unique name of the resource. The maximum length of the name is 128 Unicode characters. Required setting. |
Tenant |
The name of the tenant that owns the resource. Required setting. |
Type |
Connector type: snmp. Required setting. |
Tags |
Tags for resource search. Optional setting. |
Description |
Description of the resource. The maximum length of the description is 4000 Unicode characters. |
SNMP resource |
Settings for connecting to an SNMP resource:
You can add multiple connections to SNMP resources or delete an SNMP resource connection. To create a connection to an SNMP resource, click the + SNMP resource button. To delete a connection to an SNMP resource, click the delete |
Settings |
Rules for naming the received data, according to which OIDs (object identifiers) are converted to the keys with which the normalizer can interact. Available settings:
You can do the following with rules:
|
Advanced settings tab
Setting |
Description |
|---|---|
Debug |
The switch enables resource logging. The toggle switch is turned off by default. |
Character encoding |
Character encoding. The default is UTF-8. |
Connector, snmp-trap type
Connectors of the snmp-trap type are used for passively receiving events using SNMP traps when working with Windows and Linux agents. The connector receives snmp-trap events and prepares them for normalization by mapping SNMP object IDs to temporary keys. Then the message is passed to the JSON normalizer, where the temporary keys are mapped to the KUMA fields and an event is generated. To process events received over SNMP, you must use the json normalizer. Supported SNMP protocol versions:
- snmpV1
- snmpV2
Settings for a connector of the snmp-trap type are described in the following tables.
Basic settings tab
Setting |
Description |
|---|---|
Name |
Unique name of the resource. The maximum length of the name is 128 Unicode characters. Required setting. |
Tenant |
The name of the tenant that owns the resource. Required setting. |
Type |
Connector type: snmp-trap. Required setting. |
Tags |
Tags for resource search. Optional setting. |
Description |
Description of the resource. The maximum length of the description is 4000 Unicode characters. |
SNMP resource |
Connection settings for receiving snmp-trap events:
You can add multiple connections or delete a connection. To add a connection, click the + SNMP resource button. To remove a SNMP resource, click the delete |
Settings |
Rules for naming the received data, according to which OIDs (object identifiers) are converted to the keys with which the normalizer can interact. Available settings:
You can do the following with rules:
|
Advanced settings tab
Setting |
Description |
|---|---|
Debug |
The switch enables resource logging. The toggle switch is turned off by default. |
Character encoding |
Character encoding. The default is UTF-8. When receiving snmp-trap events from Windows with Russian localization, if you encounter invalid characters in the event, we recommend changing the character encoding in the snmp-trap connector to Windows 1251. |
Configuring the source of SNMP trap messages for Windows
Configuring a Windows device to send SNMP trap messages to the KUMA collector involves the following steps:
- Configuring and starting the SNMP and SNMP trap services
- Configuring the Event to Trap Translator service
Events from the source of SNMP trap messages must be received by the KUMA collector, which uses a connector of the snmp-trap type and a json normalizer.
To configure and start the SNMP and SNMP trap services in Windows 10:
- Open Settings → Apps → Apps and features → Optional features → Add feature → Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) and click Install.
- Wait for the installation to complete and restart your computer.
- Make sure that the SNMP service is running. If any of the following services are not running, enable them:
- Services → SNMP Service.
- Services → SNMP Trap.
- Right-click Services → SNMP Service, and in the context menu select Properties. Specify the following settings:
- On the Log On tab, select the Local System account check box.
- On the Agent tab, fill in the Contact (for example, specify
User-win10) and Location (for example, specifydetroit) fields. - On the Traps tab:
- In the Community Name field, enter community public and click Add to list.
- In the Trap destination field, click Add, specify the IP address or host of the KUMA server on which the collector that waits for SNMP events is deployed, and click Add.
- On the Security tab:
- Select the Send authentication trap check box.
- In the Accepted community names table, click Add, enter Community Name public and specify READ WRITE as the Community rights.
- Select the Accept SNMP packets from any hosts check box.
- Click Apply and confirm your selection.
- Right click Services → SNMP Service and select Restart.
To configure and start the SNMP and SNMP trap services in Windows XP:
- Open Start → Control Panel → Add or Remove Programs → Add / Remove Windows Components → Management and Monitoring Tools → Details.
- Select Simple Network Management Protocol and WMI SNMP Provider, and then click OK → Next.
- Wait for the installation to complete and restart your computer.
- Make sure that the SNMP service is running. If any of the following services are not running, enable them by setting the Startup type to Automatic:
- Services → SNMP Service.
- Services → SNMP Trap.
- Right-click Services → SNMP Service, and in the context menu select Properties. Specify the following settings:
- On the Log On tab, select the Local System account check box.
- On the Agent tab, fill in the Contact (for example, specify
User-win10) and Location (for example, specifydetroit) fields. - On the Traps tab:
- In the Community Name field, enter community public and click Add to list.
- In the Trap destination field, click Add, specify the IP address or host of the KUMA server on which the collector that waits for SNMP events is deployed, and click Add.
- On the Security tab:
- Select the Send authentication trap check box.
- In the Accepted community names table, click Add, enter Community Name public and specify READ WRITE as the Community rights.
- Select the Accept SNMP packets from any hosts check box.
- Click Apply and confirm your selection.
- Right click Services → SNMP Service and select Restart.
Changing the port for the SNMP trap service
You can change the SNMP trap service port if necessary.
To change the port of the SNMP trap service:
- Open the C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc folder.
- Open the services file in Notepad as an administrator.
- In the service name section of the file, specify the snmp-trap connector port added to the KUMA collector for the SNMP trap service.
- Save the file.
- Open the Control Panel and select Administrative Tools → Services.
- Right-click SNMP Service and select Restart.
To configure the Event to Trap Translator service that translates Windows events to SNMP trap messages:
- In the command line, type
evntwinand press Enter. - Under Configuration type, select Custom, and click the Edit button.
- In the Event sources group of settings, use the Add button to find and add the events that you want to send to KUMA collector with the SNMP trap connector installed.
- Click the Settings button, in the opened window, select the Don't apply throttle check box, and click OK.
- Click Apply and confirm your selection.
Connector, kata/edr type
Connectors of the kata/edr type are used for getting KEDR data via the API. Settings for a connector of the kata/edr type are described in the following tables.
Basic settings tab
Setting |
Description |
|---|---|
Name |
Unique name of the resource. The maximum length of the name is 128 Unicode characters. Required setting. |
Tenant |
The name of the tenant that owns the resource. Required setting. |
Type |
Connector type: kata/edr. Required setting. |
Tags |
Tags for resource search. Optional setting. |
URL |
URL that you want to connect to. The following URL formats are supported:
You can add multiple URLs or remove an URL. KUMA does not allow saving a resource or service if the URL field contains a tab or space character. To add an URL, click the + Add button. To remove an URL, click the delete Required setting. |
Secret |
Secret that stores the credentials for connecting to the KATA/EDR server. You can select an existing secret or create a new secret. To create a new secret, select Create new. If you want to edit the settings of an existing secret, click the pencil Required setting. |
External ID |
Identifier for external systems. KUMA automatically generates an ID and populates this field with it. |
Description |
Description of the resource. The maximum length of the description is 4000 Unicode characters. |
Advanced settings tab
Setting |
Description |
|---|---|
Debug |
The switch enables resource logging. The toggle switch is turned off by default. |
Character encoding |
Character encoding. We only recommend configuring a conversion if you find invalid characters in the fields of the normalized event. By default, no value is selected. |
Number of events |
Maximum number of events in one request. By default, the value set on the KATA/EDR server is used. |
Events fetch timeout |
The time in seconds to wait for receipt of events from the KATA/EDR server. Default value: |
Client timeout |
Time in seconds to wait for a response from the KATA/EDR server. Default value: |
KEDRQL filter |
Filter of requests to the KATA/EDR server. For more details on the query language, please refer to the KEDR Help. |
Connector, vmware type
Connectors of the vmware type are used for getting VMware vCenter data via the API. Settings for a connector of the vmware type are described in the following tables.
Basic settings tab
Setting |
Description |
|---|---|
Name |
Unique name of the resource. The maximum length of the name is 128 Unicode characters. Required setting. |
Tenant |
The name of the tenant that owns the resource. Required setting. |
Type |
Connector type: vmware. Required setting. |
Tags |
Tags for resource search. Optional setting. |
URL |
URL of the VMware API. You need to include the hostname and port number in the URL. You can only specify one URL. Required setting. |
VMware credentials |
Secret that stores the user name and password for connecting to the VMware API. You can select an existing secret or create a new secret. To create a new secret, select Create new. If you want to edit the settings of an existing secret, click the pencil Required setting. |
Client timeout |
Time to wait after a request that did not return events before making a new request. The default value is 5 seconds. If you specify |
Maximum number of events |
Number of events requested from the VMware API in one request. The default value is |
Start timestamp |
Starting date and time from which you want to read events from the VMware API. By default, events are read from the VMware API from the time when the collector was started. If started after the collector is stopped, the events are read from the last saved date. |
Description |
Description of the resource. The maximum length of the description is 4000 Unicode characters. |
Advanced settings tab
Setting |
Description |
|---|---|
Debug |
The switch enables resource logging. The toggle switch is turned off by default. |
Character encoding |
Character encoding. The default is UTF-8. |
TLS mode |
TLS encryption mode. When using TLS encryption, you cannot specify an IP address in the URL field on the Basic settings. Available values:
|
Connector, elastic type
Connectors of the elastic type are used for getting Elasticsearch data. Elasticsearch version 7.0.0 is supported. Settings for a connector of the elastic type are described in the following tables.
Basic settings tab
Setting |
Description |
|---|---|
Name |
Unique name of the resource. The maximum length of the name is 128 Unicode characters. Required setting. |
Tenant |
The name of the tenant that owns the resource. Required setting. |
Type |
Connector type: elastic. Required setting. |
Tags |
Tags for resource search. Optional setting. |
Connection |
Elasticsearch server connection settings:
You can add multiple connections to an Elasticsearch server resources or delete an Elasticsearch server connection. To add an Elasticsearch server connection, click the + Add connection button. To delete an Elasticsearch server connection, click the delete |
Description |
Description of the resource. The maximum length of the description is 4000 Unicode characters. |
Advanced settings tab
Setting |
Description |
|---|---|
Debug |
The switch enables resource logging. The toggle switch is turned off by default. |
Character encoding |
Character encoding. The default is UTF-8. |
Connector, office365 type
Connectors of the office365 type are used for receiving Microsoft 365 (Office 365) data via the API.
Available settings for a connector of the office365 type are described in the following tables.
Basic settings tab
Setting |
Description |
|---|---|
Name |
Unique name of the resource. The maximum length of the name is 128 Unicode characters. Required setting. |
Tenant |
The name of the tenant that owns the resource. Required setting. |
Type |
Connector type: office365. Required setting. |
Tags |
Tags for resource search. Optional setting. |
Office365 content types |
Content types that you want to receive in KUMA. The following content types are available, providing information about actions and events in Microsoft 365, grouped by information source:
You can find detailed information about the properties of the available content types and related events in the schema on the Microsoft website. Required setting. You can select one or more content types. |
Office365 tenant ID |
Unique ID that you get after registering an account with Microsoft 365. If you do not have one, contact your administrator or Microsoft. Required setting. |
Office365 client ID |
Unique ID that you get after registering an account with Microsoft 365. If you do not have one, contact your administrator or Microsoft. Required setting. |
Authorization |
Authorization method for connecting to Microsoft 365. The following authorization methods are available:
For more information, see the section on secrets. |
Office365 credentials |
The field becomes available after selecting the authorization method. You can select one of the available authorization secrets or create a new secret of the selected type. Required setting. |
Description |
Description of the resource. The maximum length of the description is 4000 Unicode characters. |
Advanced settings tab
Setting |
Description |
|---|---|
Debug |
The switch enables resource logging. The toggle switch is turned off by default. |
Character encoding |
Character encoding. The default is UTF-8. |
Authentication host |
The URL that is used for connection and authorization. By default, a connection is made to https://login.microsoftonline.com. |
Resource host |
URL from which the events are to be received. The default address is https://manage.office.com. |
Retrospective analysis interval, hours |
The period for which all new events are requested, in hours. To avoid losing some events, it is important to set overlapping event reception intervals, because some types of Microsoft 365 content may be sent with a delay. In this case, previously received events are not duplicated. By default, all new events for the last 12 hours are requested. |
Request timeout, sec |
Time to wait for a response to a request to get new events, in seconds. The default response timeout is 30 seconds. |
Repeat interval, sec |
The time in seconds after which a failed request to get new events must be repeated. By default, a request to get new events is repeated 10 seconds after getting an error or no response within the specified timeout. |
Clear interval, sec |
How often obsolete data is deleted, in seconds. The minimum value is 300 seconds. By default, obsolete data is deleted every 1800 seconds. |
Poll interval, min |
How often requests for new events are sent, in minutes. By default, requests are sent every 10 minutes. |
Proxy server |
Proxy settings, if necessary to connect to Microsoft 365. You can select one of the available proxy servers or create a new proxy server. |
 icon next to it.
icon next to it. icon next to it.
icon next to it.