Contents
SNMP protocol
You can use SNMP to collect monitoring data for equipment that does not support installing Zabbix agents. In this case, instead of the Zabbix agent, a special software entity called an SNMP agent is installed. It continuously monitors the equipment, gathering basic information about status, performance indicators, and configuration. The gathered information is then transferred to the SNMP manager, which is a centralized system that processes the received monitoring data. In Kaspersky SD-WAN, the Zabbix proxy server acts as the SNMP manager.
The SNMP protocol operates at the TCP/IP application layer (the seventh layer of the OSI model). The SNMP manager and SNMP agents exchange requests and notifications. In both cases these are standard messages. The difference lies in the direction in which the message is sent, as well as its function.
When the SNMP manager sends a message to the SNMP agent, it is used to obtain monitoring data and is called a request. By default, SNMP agents receive requests from the SNMP manager on port 161. However, the manager can send requests through any available port. The response arrives on the same port from which the request was sent.
On the other hand, if the SNMP agent sends a message to the SNMP manager, it is used to provide monitoring data and is called a notification. By default, the SNMP manager receives notifications from SNMP agents on port 162. However, agents can send notifications through any available port. Two types of notifications exist:
- Traps are notifications with information about certain events that the SNMP agent sends without a prior request from the SNMP manager. When a specified event occurs, such as a shutdown of equipment or one of its network interfaces, the SNMP agent generates a trap and sends it to the SNMP manager as a UPD message. Traps let the equipment automatically inform the SNMP manager about important events without waiting for a request.
- Inform requests are notifications similar to traps, which differ in that they require additional confirmation from the SNMP manager. When the SNMP agent sends an inform request to the SNMP manager, the agent waits to receive an acknowledgment. If the SNMP manager successfully receives and processes the inform request, it sends an acknowledgment message to the SNMP agent. The acknowledgement mechanism allows you to ensure the reliability of delivery of notifications.
When using the TLS or DTLS protocol, traps arrive on port 10162 of the SNMP manager, and information requests arrive on port 10161.
In the case of SNMP, all basic protocol data units (PDUs) have the same structure (see figure below). The IP header and UDP header are used for encapsulation and are not actually part of the protocol data unit.
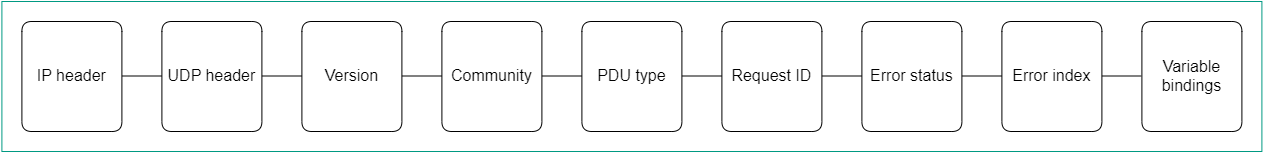
SNMP Protocol Data Unit diagram
Configuring the connection of the SNMP manager to SNMP agents
You must specify the settings for connecting the SNMP manager to SNMP agents installed on your equipment, such as CPE devices. In Kaspersky SD-WAN, the Zabbix proxy server acts as the SNMP manager.
The specified settings are used for all SNMP agents. This saves time and avoids the need to configure individual pieces of equipment. The exception is when connection settings are locally overridden on the equipment.
To configure the connection of the SNMP manager to SNMP agents:
- In the menu, go to the Infrastructure section.
The SD-WAN infrastructure management page is displayed. By default, the Network resources tab is selected, which displays the table of SD-WAN Controllers.
- Click Management next to the SD-WAN Controller and in the drop-down list, select Configuration menu.
This opens the SD-WAN Controller configuration menu. By default, you are taken to the Controller nodes section, which displays a table of Controller nodes.
- Go to the SNMP section.
A table of traps is displayed.
- In the upper part of the page, under Manager parameters, click Edit.
- This opens a window; in that window, in the Address field, enter the IP address or host name of the equipment on which the SNMP agent is installed, in the <transport protocol>:<IP address or host name>/<port number> format. For example, you can enter
udp:192.168.2.0/24. - In the Community field, enter the SNMP community string. The community string is used as a password which the SNMP manager uses to connect to SNMP agents. The default value is
public, which provides read-only access. We recommend changing the default to a more secure and unique community string to ensure reliable communication between your SNMP manager and SNMP agents.You must specify the same community string when configuring the SNMP manager connection to SNMP agents and when creating traps.
- Click Save.
Creating a trap
You can create a trap that SNMP agents must send to the SNMP manager.
To create a trap:
- In the menu, go to the Infrastructure section.
The SD-WAN infrastructure management page is displayed. By default, the Network resources tab is selected, which displays the table of SD-WAN Controllers.
- Click Management next to the SD-WAN Controller and in the drop-down list, select Configuration menu.
This opens the SD-WAN Controller configuration menu. By default, you are taken to the Controller nodes section, which displays a table of Controller nodes.
- Go to the SNMP section.
A table of traps is displayed.
- Under Trap parameters, click Edit.
- This opens a window; in that window, click Add to create a trap.
- In the Manager port field, enter the IP address or hostname of the SNMP manager. In Kaspersky SD-WAN, the Zabbix proxy server acts as the SNMP manager.
- In the Manager port field, enter the port number of the SNMP manager. The default setting is
162. - In the Community field, enter the SNMP community string. The community string is used as a password which the SNMP manager uses to connect to SNMP agents. The default value is
public, which provides read-only access. We recommend changing the default to a more secure and unique community string to ensure reliable communication between your SNMP manager and SNMP agents.You must specify the same community string when configuring the SNMP manager connection to SNMP agents and when creating traps.
- In the Allowed traps field, click Edit and select the following check boxes to select which traps SNMP agents can send to the SNMP manager:
- Select the ifUpNotification check box to have the SNMP agent send a trap to the SNMP manager when one of the network interfaces of the equipment on which the agent is installed becomes active.
- Select the ifDownNotification check box to have the SNMP agent send a trap to the SNMP manager when one of the network interfaces of the equipment on which the agent is installed becomes inactive.
- Select the swUpNotification check box to have the SNMP agent send a trap to the SNMP manager when one the equipment on which the agent is installed becomes active.
- Select the swDownNotification check box to have the SNMP agent send a trap to the SNMP manager when the equipment on which the agent is installed becomes inactive.
By default, all check boxes are selected.
- Click Back to continue specifying settings.
- In the Description field, enter a brief description of the trap.
- Click Save.
The trap is created and displayed in the table.
Page topEditing a trap
To edit a trap:
- In the menu, go to the Infrastructure section.
The SD-WAN infrastructure management page is displayed. By default, the Network resources tab is selected, which displays the table of SD-WAN Controllers.
- Click Management next to the SD-WAN Controller and in the drop-down list, select Configuration menu.
This opens the SD-WAN Controller configuration menu. By default, you are taken to the Controller nodes section, which displays a table of Controller nodes.
- Go to the SNMP section.
A table of traps is displayed.
- Under Trap parameters, click Edit.
- This opens a window; in that window, edit the settings that you want to change. For a description of the settings, see instructions for creating a trap.
- Click Save.
Deleting a trap
Deleted traps cannot be restored.
To delete a trap:
- In the menu, go to the Infrastructure section.
The SD-WAN infrastructure management page is displayed. By default, the Network resources tab is selected, which displays the table of SD-WAN Controllers.
- Click Management next to the SD-WAN Controller and in the drop-down list, select Configuration menu.
This opens the SD-WAN Controller configuration menu. By default, you are taken to the Controller nodes section, which displays a table of Controller nodes.
- Go to the SNMP section.
A table of traps is displayed.
- Under Trap parameters, click Edit.
- This opens a window; in that window, click Delete next to the trap.
- Click Save.
The trap is deleted and is no longer displayed in the table.
Page top